

TIRADS Reporting guidelines for thyroid nodules:
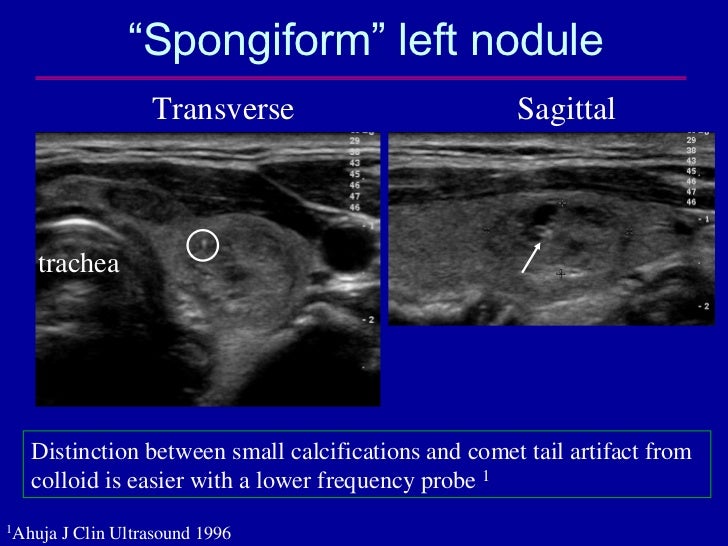
Additional benign appearances are not included in the lexicon, for eg.The presence of “halo” is not specific and is not included in the lexicon.Doppler has not found to be useful in distinguishing benign from malignant lesions, however, the presence of vascularity rules out debris and hemorrhage which are inconsequential.TIRADS ACR categories TIRADS ACR classificationĭownload a ready to print image of the TIRADS categories $ Punctate echogenic foci are non-shadowing. # “Large comet-tail artifacts” are defined as echogenic foci with V-shaped echoes >1 mm deep to them. *Spongiform nodule should be composed predominantly (>50%) of cystic spaces. Following criteria have been described:.Thyroid nodules are evaluated on certain sonographic criteria, each criterion is allotted points which are summed up and then each nodule is categorized in one of the above-mentioned categories, depending on the score.Alternatively, you can use this image provided by the ACR online : ACR TI-RADS Click here for a ready to print image of the table. One need not memorize this table, instead, you can print a copy of this TI RADS chart and put it up near your reporting station.Alternatively, you can use this image provided by the ACR online : Similar to the BI-RADS classification, thyroid nodules on ultrasound are classified according to the risk of malignancies into the following categories :ĭownload a ready to print image of the TIRADS classification.These guidelines provide criteria and recommendations for follow-up and biopsy of thyroid nodules.
#COMET TAIL ARTIFACT MEANING FULL#
The full text of this article is available here: ACR TI-RADS white paper 2017 pdf. The guidelines have been described as per the ACR TI-RADS 2017 radiology white paper.Develop a standardized TI-RADS risk-stratification system based on the lexicon to inform practitioners about which nodules warrant a biopsy.Produce a lexicon to describe all thyroid nodules on sonography.Develop management guidelines for nodules that are discovered incidentally on CT, MRI, PET or ultrasound.ACR Committee for TI-RADS has the following objectives :.A recent study published in AJR confirms that the ACR TI-RADS performs well as compared to other scoring systems. Different variations of the TI-RADS classifications and recommendations are available, the most commonly followed one is the ACR TI-RADS.It consists of guidelines regarding whether a thyroid nodule should be followed up on ultrasound or to should be biopsied. It is a reporting system for thyroid nodules on Ultrasound formulated by the ACR, akin to BI-RADS developed for breast ultrasounds. TI-RADS stands for Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System. What is TIRADS / ti rads / TI-RADS and what does it stand for? Unnecessary biopsies can result in a burden on the healthcare system without significant benefits. Hence it is essential to evaluate which of these nodules actually need a fine needle aspiration cytology (FNAC)/biopsy, which is the most effective method currently to diagnose whether a particular nodule is worrisome. Also, the mortality associated with papillary thyroid carcinomas has remained low.

Even the smaller malignant nodules have an indolent course. With the advent of high-resolution ultrasound, the number of thyroid nodules being detected is increasing.TIRADS examples with scoring: Test yourself!.Thyroid Ultrasound Reporting Template using ACR TIRADS


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
